
Cassandra Installation on CentOS 7.x
Before Installing Cassandra, we need to Install Java 8;
yum update -y
wget –no-cookies –no-check-certificate –header “Cookie:oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie” “http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u131-b11/d54c1d3a095b4ff2b6607d096fa80163/jdk-8u131-linux-x64.rpm”
yum -y localinstall jdk-8u131-linux-x64.rpm
We can check java version as down below;
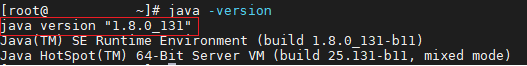
To install Cassandra, we need to add following parameters into /etc/yum.repos.d/cassandra.repo
[cassandra]
name=Apache Cassandra
baseurl=https://www.apache.org/dist/cassandra/redhat/311x/
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://www.apache.org/dist/cassandra/KEYS
You can use “vi” command to enable to insert as down below;
vi /etc/yum.repos.d/cassandra.repo
Now, we can install Cassandra;
yum install cassandra -y
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start cassandra
systemctl enable cassandra
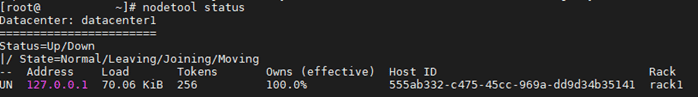
You can verify that Cassandra is running by typing the following command;
nodetool status
Cassandra comes with command line shell cqlsh to run query.
To access CQL shell, run the following command.
[root@ ~]# cqlsh
Connected to Test Cluster at 127.0.0.1:9042.
[cqlsh 5.0.1 | Cassandra 3.11.0 | CQL spec 3.4.4 | Native protocol v4]
Use HELP for help.
Cassandra – Create KeySpace (Database)
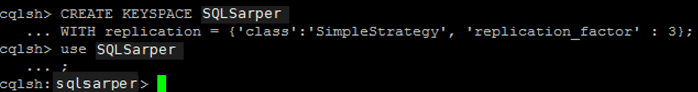
After run the command “cqlsh”, we are now able to create KeySpace as down below;
CREATE KEYSPACE SQLSarper WITH replication = {‘class’:’SimpleStrategy’, ‘replication_factor’ : 3};
We created a keyspace “SQLSarper”, now we can Access into the keyspace with following command;
Use SQLSarper;
Now we can create our objects.
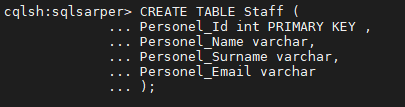
Let’s create a table on SQLSarper KeySpace;
After Access into SQLSarper KeySpace with “use SQLSarper” command, we can create our table;
CREATE TABLE Staff (
Personel_Id int PRIMARY KEY ,
Personel_Name varchar,
Personel_Surname varchar,
Personel_Email varchar
);
ALTER TABLE
Add Colomn;
ALTER TABLE Staff
ADD Adress text ;
We can check the table with “SELECT * FROM Staff ;”
Drop Colomn;
ALTER TABLE Staff
DROP Adress ;
DROP TABLE
–Create a table
CREATE TABLE Deneme
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Text text
);
–Insert data into the table
INSERT INTO Deneme (ID,Text) VALUES (1,’SarperERKOL’);
— Check the table
SELECT * FROM Deneme;
–Delete the table
DROP TABLE Deneme;
TRUNCATE TABLE
TRUNCATE TABLE Personel;
Tags: